HbA1c (Glycated Haemoglobin)
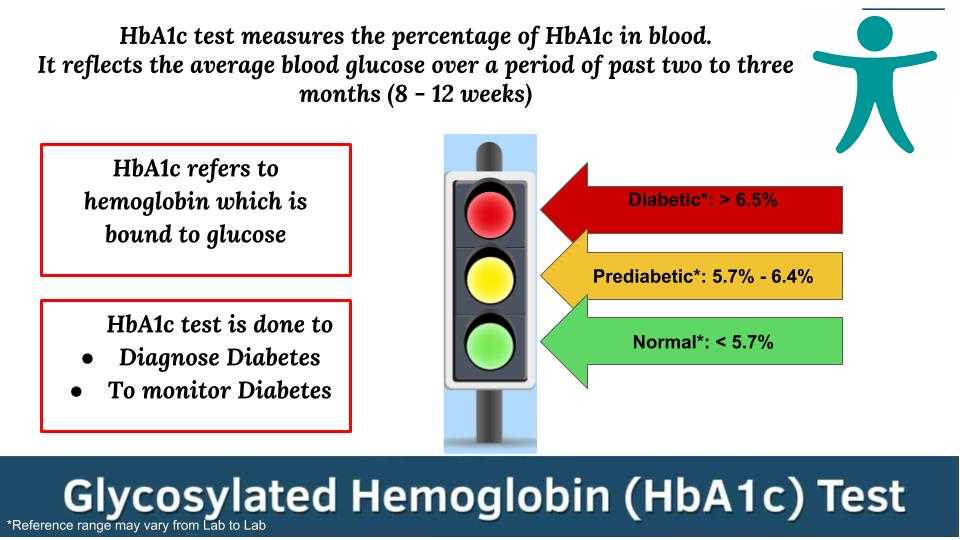
Glycosylated Hemoglobin, also called Glycated Hemoglobin, Hemoglobin A1c, or HbA1c, refers to hemoglobin which is bound to glucose. Glycosylated Hemoglobin Test is performed to measure the percentage of glycosylated hemoglobin in blood which reflects the average blood glucose over a period of past two to three months (8 - 12 weeks).
- No special preparation required
The Glycosylated Hemoglobin test is performed to:
Monitor Diabetes treatment efficacy by measuring glycosylated hemoglobin regularly
Screen for Diabetes as part of regular health checkup, as well as in patients with high risk of developing diabetes
Diagnose and confirm diabetes in combination with other tests if blood sugar levels are high over a long period of time
Normal: Below 5.7% (39 mmol/mol approx.)
Prediabetic: 5.7% - 6.4% (39 to 46 mmol/mol approx.)
Diabetic: Above 6.5% (above 48 mmol/mol approx.)
Less than 5.7% Glycated Hemoglobin indicates normal levels of blood sugar. Increased risk of developing Diabetes is found in Prediabetic patients with blood sugar level between 5.7% and 6.4%. Patients with a HbA1c level greater than 6.5% are usually diagnosed with Diabetes.
Hemoglobin is the protein found in Red Blood Cells and is responsible for transporting oxygen. Of the different types of hemoglobin, Hemoglobin A is predominant. With elevation of blood sugar levels, some glucose binds spontaneously to Hemoglobin A (this binding is called Glycosylation or Glycation) and remains bound for the complete lifetime of the RBC, which is 120 days normally. Higher the level of glucose in the blood, greater is the amount of it binding to Hemoglobin A. Hemoglobin A1c is the dominant form of Glycated Hemoglobin. As RBCs die and are replaced, Hemoglobin A1c is cleared and slowly replaced with non-glycosylated hemoglobin. Measurement of HbA1c level over a period of time gives an indication of the level of glucose in the blood over the specified period of time. This helps in the diagnosis of Diabetes and is useful for monitoring the effectiveness of measures taken to reduce blood sugar levels.
Common questions regarding 'Glycosylated Hemoglobin'