(Urate)
Uric acid is a nitrogenous compound which is formed as a byproduct of metabolic activities and is eliminated by the kidneys. The buildup of uric acid levels in blood gives rise to a number of health conditions. The Uric Acid Test is performed to measure the levels of uric acid in the blood.
- No special preparation required
The Blood Uric Acid Test is performed:
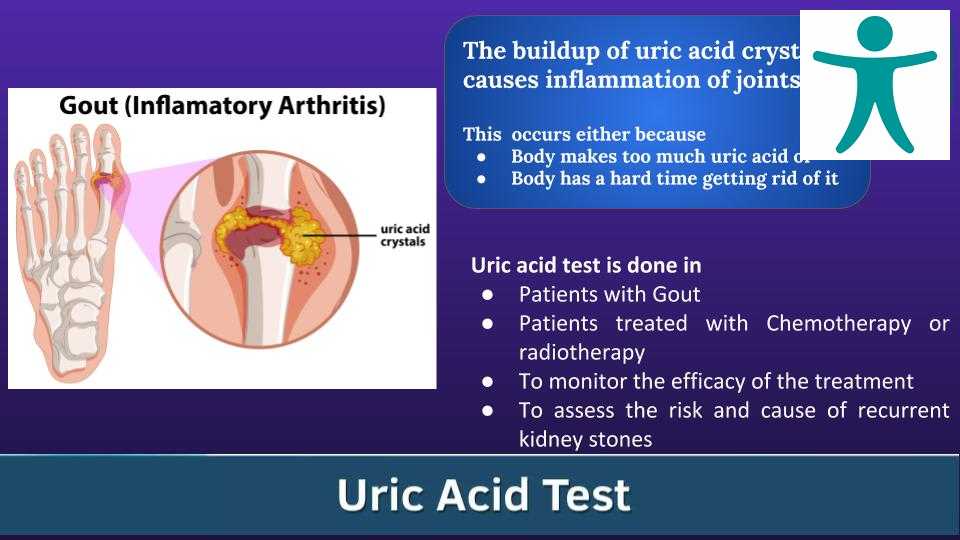
· To diagnose gout upon the appearance of symptoms
· In cancer patients being treated by chemotherapy or radiotherapy to monitor their uric acid levels
· To check the efficacy of medications that lower uric acid levels
· To assess the risk of kidney stones or to determine the cause of recurrent kidney stones
Normal uric acid range:
· Adult Female: 2.4 to 6.0 mg/dL
· Adult Male: 3.4 to 7.0 mg/dL
· Children: 2.0 to 5.5 mg/dL
Higher than normal levels of uric acid in the blood is called Hyperuricemia and may be caused due to kidney diseases, gout, chemotherapy or radiotherapy treatment.
Uric acid is a nitrogenous compound produced by the metabolic breakdown of purine. Purines are nitrogenous bases in DNA forming parts of the structural framework of the cells. Breakdown of purines occurs when cells become old and die, forming uric acid. Uric acid is also formed from the metabolic breakdown of some types of food like red meat, seafood, beans, etc.
Most of the uric acid in the blood is filtered and eliminated by the kidneys and a small remaining amount in the stool. The concentration of uric acid in the blood can increase due to overproduction of uric acid or improper elimination of uric acid, and this condition is called Hyperuricemia. Hyperuricemia can also be caused due to cancer treatment by chemotherapy or radiotherapy. These treatment methods kill the cancer cells, which may leak the uric acid into the blood.
Excess uric acid can form crystals in the synovial fluid between the joints causing inflammation and pain. This condition is called gout and can severely damage the joints if left untreated. Blood Uric Acid Test can indicate the presence of gout, or risk of formation of gout. However, it is not a definitive test for gout. Confirmatory test for gout is performed by analysis of synovial fluid (joint fluid) for monosodium urate crystals. Chronic Hyperuricemia can cause the formation of tophi, which are hard lumpy deposits of uric acid crystals formed under the skin, in the joints, and at the top of the ears. Tophi cause severe damage to the joints and may compress nerves causing chronic pain and disfigurement. The excess uric acid may also deposit and crystallize in the kidneys causing kidney stones and acute renal failure.
Common questions regarding 'Uric Acid'